親愛的會員您好,
代轉發資訊如附檔,提供大家踴躍參加,謝謝。
活動宗旨:
為擴大推廣「私有建築物耐震弱層補強」,本中心預計培訓弱層補強推動人員,為民眾提供法令解說、協助案件住戶整合意願,特辦理此教育訓練。
本中心將依推動人員各階段輔導進度,核予推動費,藉以激勵推動人員提供弱層補強宣導、諮詢、輔導、整合等服務,加速老舊建築物之補強,以達減少地震災害之目的。
活動資訊:
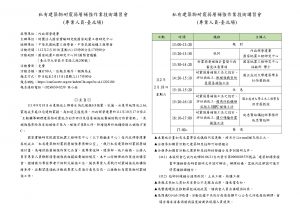
(一)活動時間:112年4月10日(星期一)13時30分
(二)活動地點:國家地震工程研究中心-台南實驗室101會議室(台南市歸仁區中正南路一段2001號)
(三)報名網址:https://conf.ncree.org.tw/index.aspx?n=A11204100 (報名人數上限80人)
*此活動無法申請建築師、技師及公務人員積分(點),敬請注意
報名相關問題聯繫窗口:02-6630-5185高先生
敬祝 安好
中華民國結構工程學會 敬啟-03/29/2023
附件: